T - Algorithms
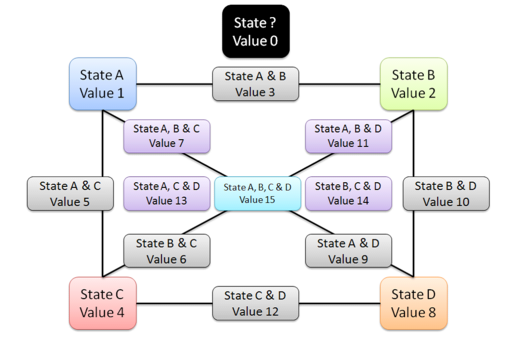
Of course, not all four main states have to be used. The same remark can be done for intermediate states.
However, states 1 and 2 have to be used.
Example: if character T1 is the "Existence of ascospores", state 1 can be "Absence of ascospores", state 2 can be "Presence of ascospores" and state 3 "Ascospores variable".
When comparing data, states A, B, C and D are considered as different (Sim = 0).
When intermediary states are compared, and one of the main states is common then the similarity is equal to 1.
For example, comparing “B&C” with “C&D” returns 1 because state C is common.
T algorithm produces comparisons that are symmetrical (Sab=Sba), but not necessarily transitive.
Suitable for identification and classification purpose.

