D - Algorithms
For D characters, the two value of the OTU's are compared.
If OTU1 has the same value then OTU2 (plus or minus the tolerance (Z) of the character) then the similarity is equal to 1. Otherwise it is equal to 0.
Example: if OTU1 has a value of 26 and OTU2, a value of 28 then Sm = 1 if Z>=2, and Sm = 0 if Z<2.
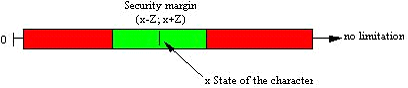
If OTU2+Z >= OTU1 >= OTU2-Z then Sm = 1
If OTU2+Z < OTU1 or OTU1 < OTU2-Z then Sm = 0
If one or both OTU's have not been encoded then the character will not be accounted ('?')
Where Z is the tolerance, a positive numeric value. This value can be changed by the user and can be different for all characters.
D algorithm produces comparisons that are symmetrical (Sab=Sba), but not necessarily transitive except if Z=0. Suitable for identification and classification purpose.

